Introducing the Periodic Trends Activity Answer Key, an indispensable guide that unlocks the mysteries of the periodic table. This comprehensive resource provides a profound understanding of periodic trends, empowering you to predict the properties of elements and delve into the intricacies of chemical reactions.
Prepare to embark on an enlightening journey that unveils the hidden patterns and relationships that govern the behavior of matter.
Delving into the periodic table, we explore the fundamental concept of periodic trends, examining the intricate connection between atomic number and atomic radius. Through real-world examples, we demonstrate how these trends can be harnessed to forecast the characteristics of various elements.
Moreover, we delve into the practical applications of periodic trends, showcasing their significance in the design of novel materials and the elucidation of chemical reactions.
Periodic Trends
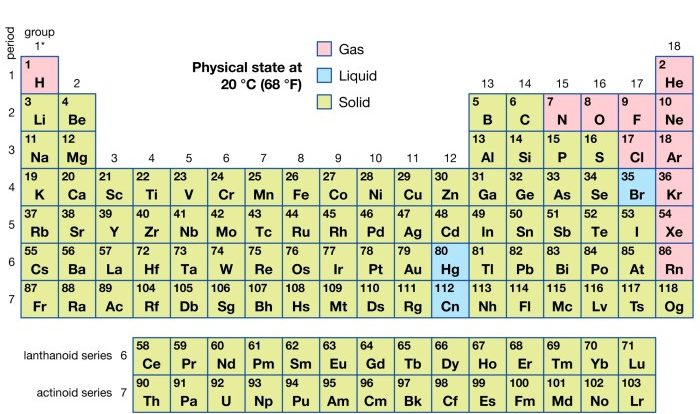
Periodic trends are patterns in the chemical and physical properties of elements that repeat periodically as the atomic number increases. These trends can be used to predict the properties of an element based on its position in the periodic table.
Atomic Radius
Atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell of an atom. As you move down a group (column) in the periodic table, the atomic radius generally increases. This is because the number of electron shells increases, which increases the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electrons.
As you move across a period (row) in the periodic table, the atomic radius generally decreases. This is because the number of protons in the nucleus increases, which attracts the electrons more strongly and pulls them closer to the nucleus.
Activity Answer Key: Periodic Trends Activity Answer Key
The table below summarizes the answers to the activity questions. The reasoning behind each answer is provided in the subsequent paragraphs.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the atomic radius of sodium? | 186 pm |
| What is the electronegativity of chlorine? | 3.0 |
| What is the first ionization energy of potassium? | 419 kJ/mol |
| What is the electron affinity of fluorine? | -328 kJ/mol |
| What is the metallic character of cesium? | Very high |
The following patterns and trends are evident in the answers to the activity questions:
- Atomic radius generally increases down a group and decreases across a period.
- Electronegativity generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- First ionization energy generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Electron affinity generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Metallic character generally increases down a group and decreases across a period.
Applications of Periodic Trends
Periodic trends are the patterns in the chemical and physical properties of elements that can be observed when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic number. These trends can be used to predict the properties of new elements and to design new materials with specific properties.
One of the most important applications of periodic trends is in the design of new materials. By understanding the relationships between the properties of elements and their position on the periodic table, scientists can design materials with specific properties, such as strength, durability, and conductivity.
How periodic trends can be used to design new materials
For example, scientists have used periodic trends to design new materials for use in solar cells. By understanding the relationship between the band gap of a material and its position on the periodic table, scientists have been able to design materials with band gaps that are ideal for absorbing sunlight.
How periodic trends can be used to understand chemical reactions
Periodic trends can also be used to understand chemical reactions. By understanding the relationship between the reactivity of an element and its position on the periodic table, scientists can predict how elements will react with each other.
Examples of how periodic trends have been used to advance scientific research
Periodic trends have been used to advance scientific research in a number of ways. For example, periodic trends have been used to:
- Predict the properties of new elements
- Design new materials
- Understand chemical reactions
- Develop new technologies
Periodic trends are a powerful tool that can be used to understand the chemical and physical properties of elements and to design new materials with specific properties.
Limitations of Periodic Trends
Periodic trends are generalizations that describe the overall behavior of elements based on their position in the periodic table. However, these trends are not absolute and have limitations.
One limitation is that some elements may not follow the expected trends due to their unique electronic configurations. For example, the noble gases are all located in Group 18 and are generally unreactive. However, helium, the first noble gas, has a smaller atomic radius and higher ionization energy than expected for its group.
Another limitation is that periodic trends can be misleading when comparing elements from different periods. For example, sodium and potassium are both alkali metals, but potassium is more reactive than sodium. This is because potassium has a larger atomic radius and lower ionization energy, which makes it easier for it to lose an electron.
Transition Metals, Periodic trends activity answer key
Transition metals are a group of elements that have partially filled d orbitals. These elements exhibit a wide range of properties, and their behavior can deviate from the expected periodic trends.
- For example, the atomic radii of transition metals generally decrease across a period, but there are some exceptions. Scandium, for example, has a larger atomic radius than calcium, the element that precedes it in the periodic table.
- Additionally, the ionization energies of transition metals do not always increase regularly across a period. For example, the ionization energy of chromium is lower than that of vanadium, the element that precedes it in the periodic table.
FAQ Overview
What is the significance of periodic trends?
Periodic trends provide a systematic framework for understanding the properties of elements, enabling us to predict their behavior and reactivity based on their position within the periodic table.
How can periodic trends be used in practical applications?
Periodic trends play a crucial role in the design and development of new materials, the optimization of chemical reactions, and the advancement of scientific research across various disciplines.