Periodicity and the periodic table lab – Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of periodicity and the periodic table, a fundamental framework that unravels the mysteries of chemical elements. This exploration promises to illuminate the periodic trends that govern atomic properties, unveiling the profound significance of the periodic table as a tool for comprehending the natural world and solving real-world problems.
Through a hands-on laboratory experiment, we delve into the practical applications of periodicity, witnessing firsthand how this concept has revolutionized fields ranging from chemistry to biology. Prepare to be amazed as we uncover the secrets of the periodic table, empowering you with a deeper understanding of the building blocks of our universe.
Periodicity: The Foundation of the Periodic Table
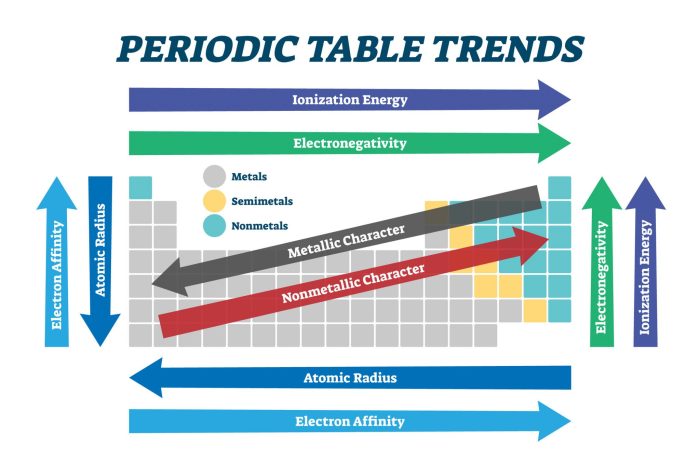
Periodicity is a fundamental concept in chemistry that describes the recurring patterns in the properties of elements as their atomic numbers increase. This pattern forms the basis of the periodic table, which organizes elements based on their periodicity.
Periodicity arises from the regular variation in the electronic configurations of elements. As you move across a period (row) in the periodic table, the number of electrons in the outermost shell increases. This leads to gradual changes in atomic properties such as atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity.
Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties
- Atomic Radius:Generally decreases across a period from left to right as the number of protons and electrons increases, resulting in a stronger electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and the electrons.
- Ionization Energy:Increases across a period from left to right as the number of protons increases, making it more difficult to remove an electron.
- Electronegativity:Increases across a period from left to right as the number of protons increases, indicating a greater attraction for electrons.
Periodic Table: A Tool for Understanding Elements
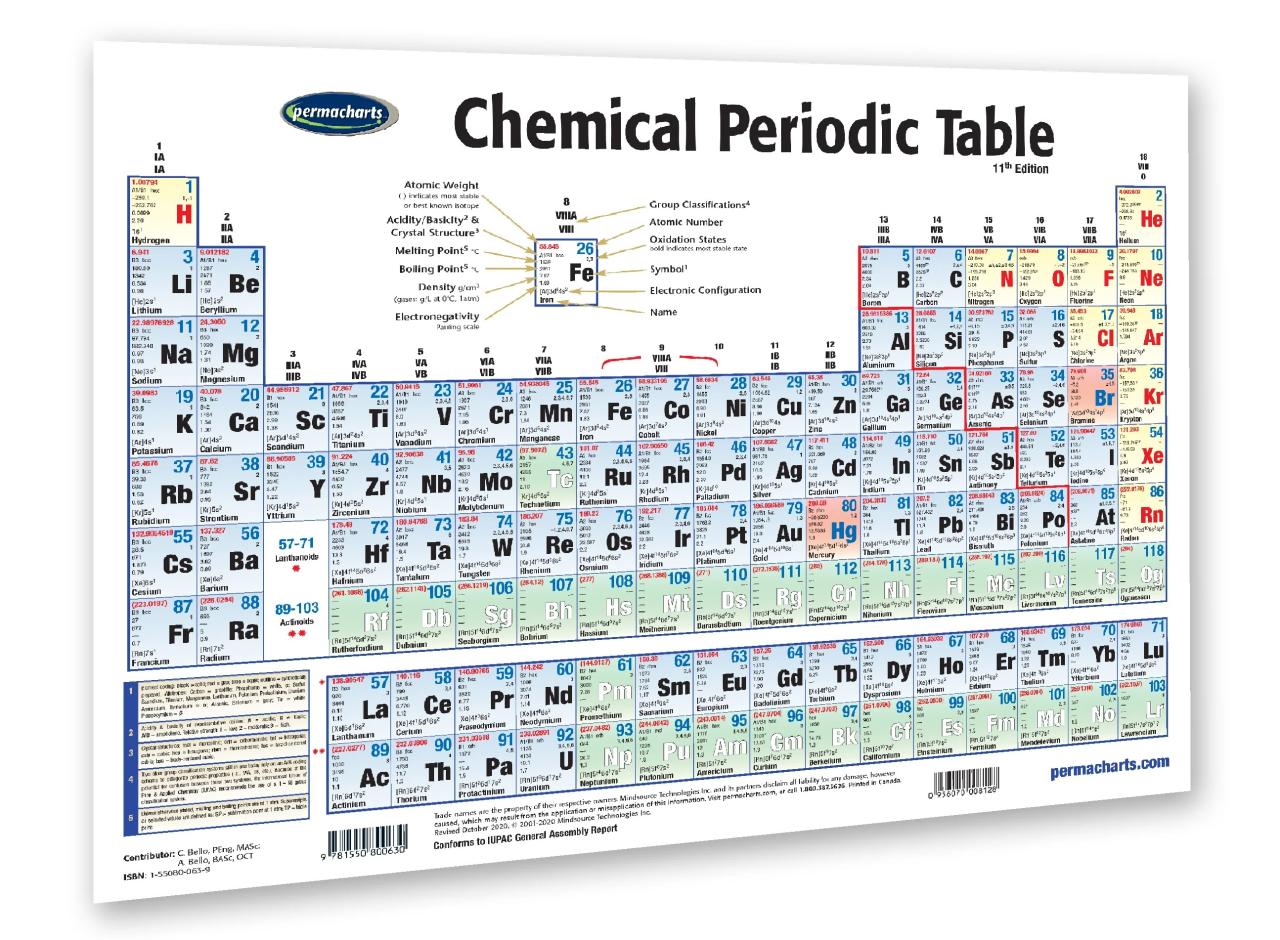
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of elements organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. It consists of 18 vertical columns (groups) and 7 horizontal rows (periods).
Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties due to having the same number of valence electrons. Elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
Using the Periodic Table to Predict Properties
The periodic table allows us to predict the properties of an element based on its position in the table. For example, elements in the alkali metal group (Group 1) are highly reactive and form 1+ ions. Halogens (Group 17) are highly electronegative and form 1- ions.
The periodic table has also been instrumental in discovering new elements and understanding chemical reactions. By identifying gaps in the table, scientists have been able to predict the existence and properties of undiscovered elements.
Periodicity in the Laboratory: A Hands-on Exploration: Periodicity And The Periodic Table Lab
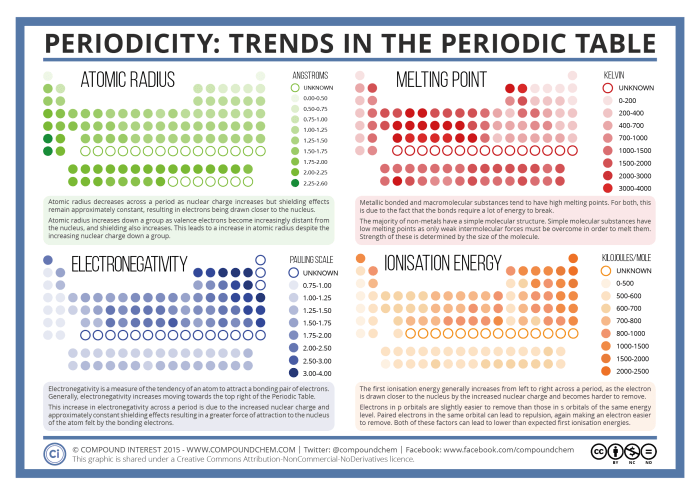
Experiment:Investigating the Periodic Trend of Atomic Radius
Procedures:
- Measure the atomic radii of selected elements using a variety of techniques, such as X-ray diffraction or ionic radii tables.
- Plot the atomic radii against the atomic numbers of the elements.
Observations:The graph will show a general decrease in atomic radius across a period from left to right.
Conclusions:The experiment demonstrates the periodicity of atomic radius and supports the concept that the properties of elements vary in a regular pattern based on their position in the periodic table.
Beyond the Classroom: Applications of Periodicity
Periodicity has wide-ranging applications in various fields, including:
Chemistry, Periodicity and the periodic table lab
- Inorganic Chemistry:Understanding the periodic trends helps predict the reactivity and bonding behavior of elements.
- Organic Chemistry:Periodicity aids in understanding the electronic structure and properties of organic compounds.
Materials Science
- Materials Design:Periodicity guides the selection and combination of elements to create materials with desired properties.
- Nanotechnology:Understanding periodicity at the nanoscale enables the design and synthesis of novel nanomaterials.
Biology
- Biochemistry:Periodicity helps explain the structure and function of biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids.
- Medicine:Periodicity aids in drug design and understanding the interactions between drugs and biological systems.
Q&A
What is periodicity?
Periodicity refers to the recurring patterns observed in the properties of elements as we move across the periodic table. These patterns are attributed to the periodic repetition of electron configurations, which govern the chemical behavior of elements.
How can the periodic table be used to predict the properties of an element?
The periodic table allows us to predict the properties of an element based on its position within the table. Elements within the same group (vertical column) share similar chemical properties due to having the same number of valence electrons. Similarly, elements within the same period (horizontal row) exhibit gradual changes in properties as the atomic number increases.
What are some practical applications of periodicity?
Periodicity finds wide-ranging applications in various fields. In chemistry, it aids in predicting the reactivity and stability of compounds. In materials science, it guides the design of new materials with tailored properties. In biology, it helps explain the structure and function of biomolecules.